Obesity is a Chronic Disease! The Complications of Obesity are the Real Issue Behind Gaining Weight When Trying to Lose It
The Primary Causes of Modern Obesity
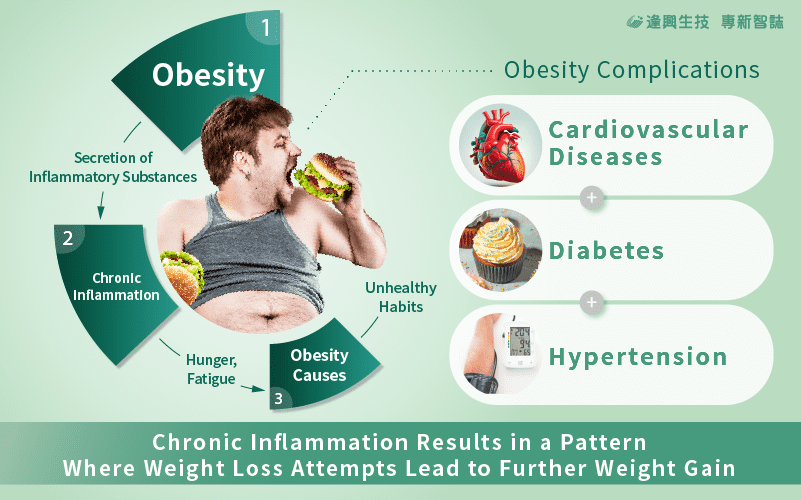
Obesity has emerged as a significant global public health concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a 30% global prevalence of overweight and obesity[1]. Research suggests that individuals grappling with modern-day stress and demanding lifestyles often resort to seeking solace in comfort foods and sugary beverages, leading to a sustained surplus of calorie intake and consequent weight gain, ultimately culminating in obesity. This progression is associated with a heightened risk of complications, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and hypertension. According to the World Obesity Atlas 2023, a failure to address obesity promptly could result in healthcare expenditures related to obesity reaching an alarming US$4.3 trillion by 2035, amounting to nearly 3% of the global GDP[2]. Primary contributors to the rising prevalence of obesity are Westernized diets, consumption of refined foods, and sedentary lifestyles[3]. Consequently, the adoption of a healthy dietary lifestyle stands out as a pivotal strategy in the battle against obesity.
Beware of Chronic Inflammation: Stuck in a Vicious Cycle, Efforts to Lose Weight Can Paradoxically Lead to Further Weight Gain.
Obesity has been established as a significant risk factor for various chronic diseases, primarily due to its role in inducing a state of inflammation within the body. The abnormal expansion of fat tissues resulting from excessive caloric intake triggers the secretion of numerous inflammatory substances, such as TNF-α and IL-6. When these substances surpass their physiological balance, they initiate an inflammatory response, setting off a vicious cycle of chronic inflammation and obesity[4][5]. If not addressed at its core, this cycle can perpetuate weight gain despite efforts to lose it, leading to complications associated with obesity and a deterioration of the body’s overall condition.
[1] Malik VS, Hu FB. The role of sugar-sweetened beverages in the global epidemics of obesity and chronic diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022;18(4):205-218. doi:10.1038/s41574-021-00627-6
[2] 對抗肥胖的「重量級」投資商機
https://money.udn.com/money/amp/story/5618/7421989
[3] 關於過重與肥胖
https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/List.aspx?nodeid=1757
[4] Monteiro LB, Prodonoff JS, Favero de Aguiar C, et al. Leptin Signaling Suppression in Macrophages Improves Immunometabolic Outcomes in Obesity. Diabetes. 2022;71(7):1546-1561.
[5] 「好累」都是「發炎」搞的鬼!一分鐘鑑定身體在發炎嗎?
https://heho.com.tw/archives/62130
Anxious About Side Effects in Managing Obesity-Related Issues? Embrace a Fresh, Healthy Approach with Plant-Derived Ingredients
Risks Linked to Unhealthy Weight Reduction Practices
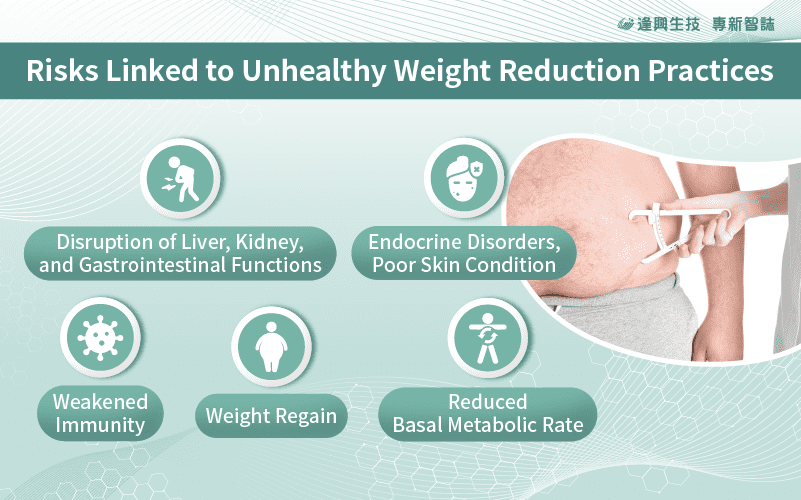
Recognized as a chronic disease, obesity prompts various interventions ranging from exercise and lifestyle modifications to surgical procedures or medications for weight loss. Nevertheless, these expedited weight loss approaches entail several health risks[6], including:
- Rapid Weight Regain:
Swift weight loss via dieting results in the loss of water and muscle mass in the body. Consequently, the body triggers a protective mechanism, prompting the energy balance system in the brain to release hunger signals. This continuous feeling of hunger may compel individuals to eat more, exacerbating the situation.
- Reduced Metabolic Rate:
When caloric intake falls below the basic requirements of the human body, the basal metabolic rate decreases to sustain essential physiological functions and conserve the body’s basic caloric expenditure. Upon returning to a regular diet, calories may not be expended rapidly, resulting in the accumulation of fat.
- Weakened Immunity:
Restrictive dieting can result in inadequate nutritional intake, accelerated breakdown of muscle proteins, diminished physical strength, decreased lymphocyte production, and compromised immunity. This heightens the susceptibility to conditions such as colds, back pain, and other illnesses.
- Disruption of Liver, Kidney, and Gastrointestinal Functions:
Sustained periods of hunger can disrupt digestive functions, while recurrent cycles of weight gain and loss may lower metabolic rates, impacting gastrointestinal function and potentially resulting in indigestion or gastrointestinal diseases.
- Poor Skin Condition and Hair Loss:
Disrupted metabolism and recurrent weight loss can result in rough and deteriorated skin, dry and discolored hair, and, in severe instances, hair loss.
Beyond the previously mentioned concerns, swift weight loss in women can impact hormone regulation, potentially leading to amenorrhea or menstrual irregularities. Thus, addressing chronic inflammation is crucial to preventing recurrent obesity and tackling the issue at its core.
A Safe and Healthy Approach to Weight Loss: Opt for Appropriate Dietary Supplements for Chronic Inflammation- Natural Herb Extract
Choosing the right health supplement is a popular approach for many individuals seeking weight loss, particularly beneficial for those dealing with obesity. Current research highlights the significance of natural herb extracts containing phytonutrients—natural compounds found in plants—that offer a range of health benefits, including the regulation of physiological functions and overall well-being. Numerous studies support the idea that phytonutrients play a role in adjusting the body’s constitution, fortifying its resilience, and enhancing metabolism[7][8]. Wel-Bloom introduces Wel-TriGo™, a natural compound that combines three plant-derived ingredients, containing various phytonutrients in an optimal ratio for maximal synergistic effect. By harnessing the power of Wel-TriGo™, Wel-Bloom collaborates with you to navigate the vast opportunities in the weight loss market. Together, we strive to create a side-effect-free, natural supplement for inflammation reduction that aids in adjusting the body’s constitution, offering a holistic and effective solution for weight management.
[6] 減肥瘦太快,當心對身體造成5大影響
https://heho.com.tw/archives/175373
[7] Saad, B. (2022). Prevention and Treatment of Obesity-Related Inflammatory Diseases by Edible and Medicinal Plants and Their Active Compounds. Immuno, 2(4), 609-629.
[8] 認識植化素
http://www.asanga.com.tw/article.php?BlogID=26&lang=zh
